| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
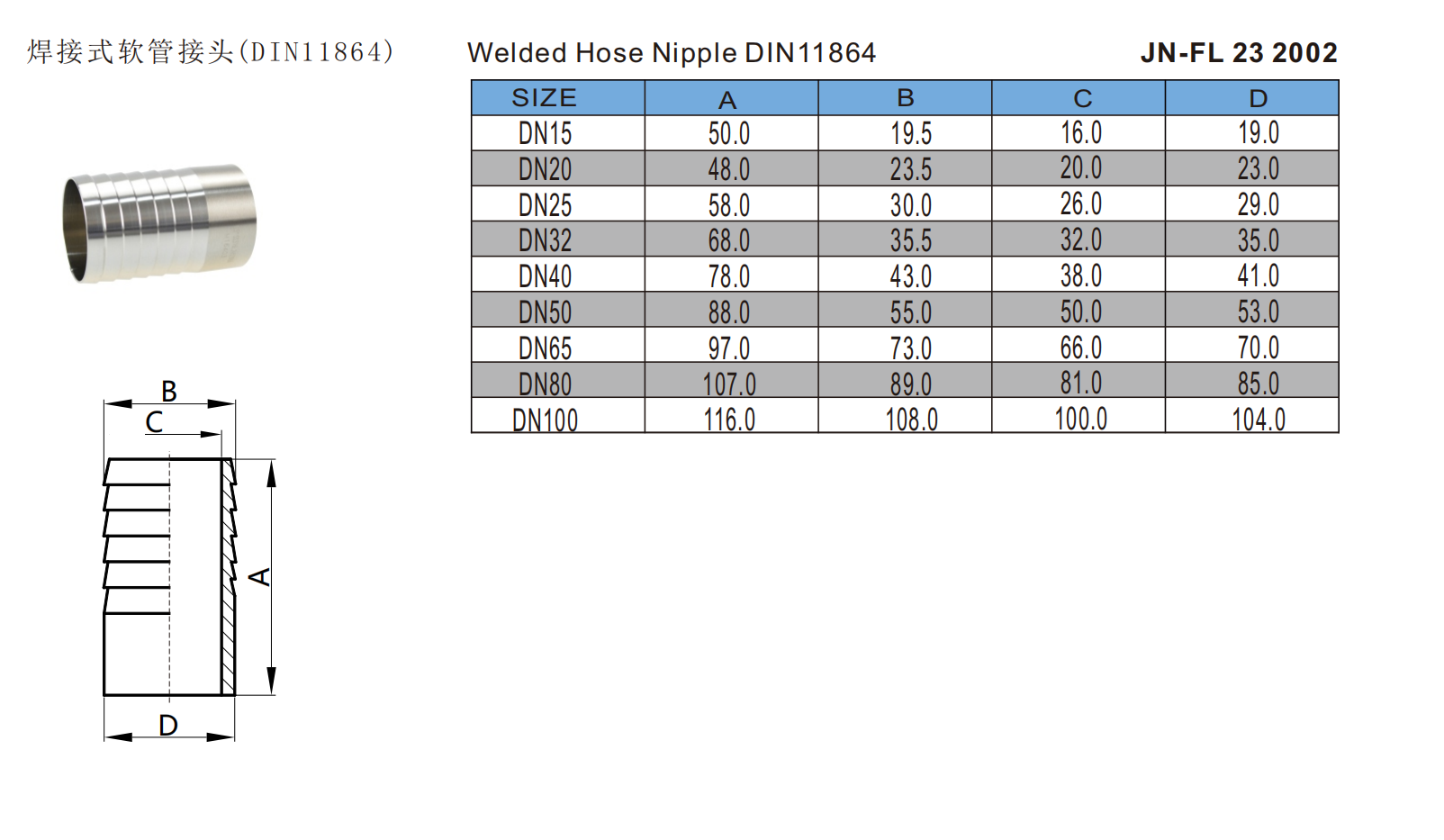
JN-FL 23 2002
JONENG
7307290000








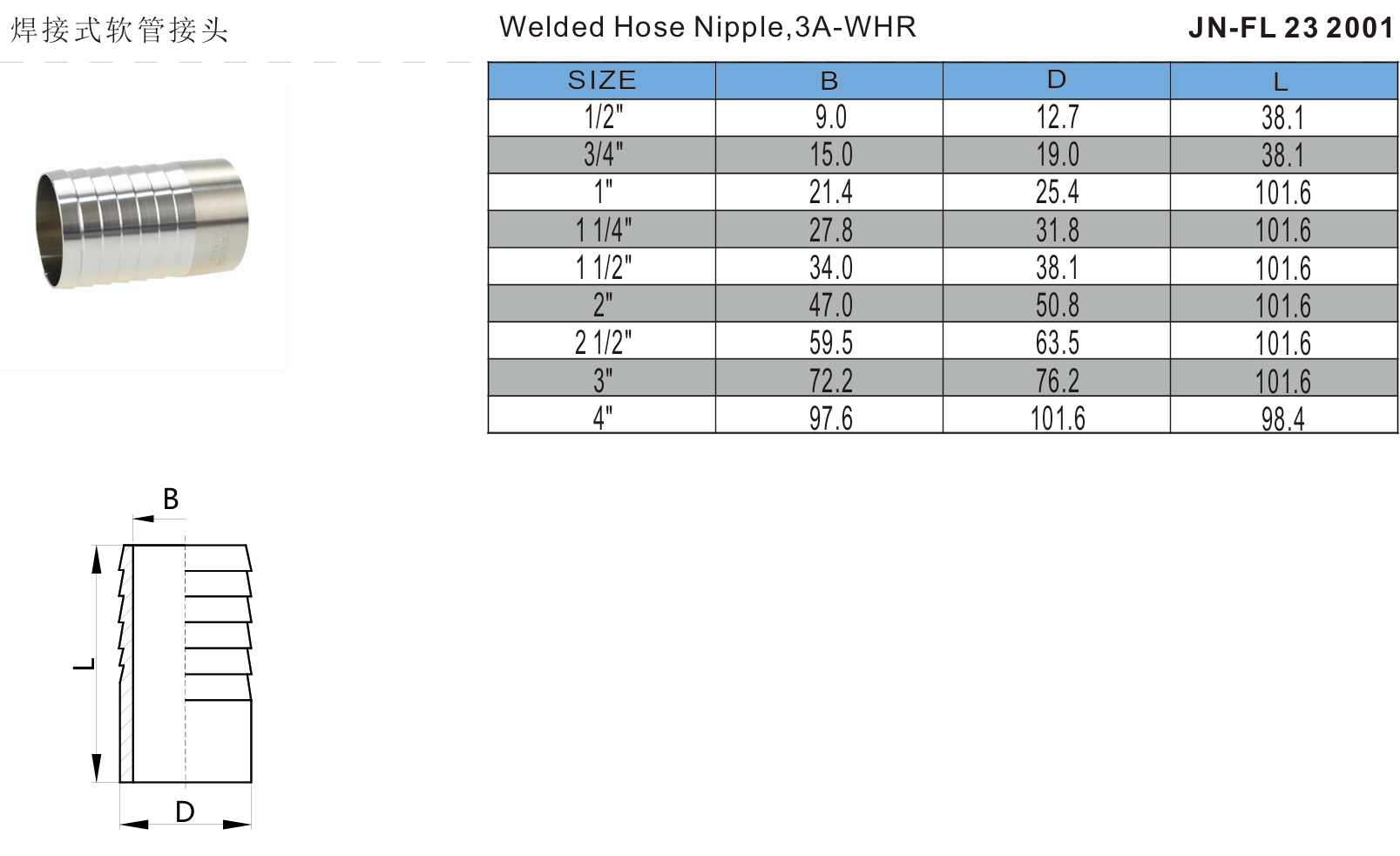
304 Stainless Steel Sanitary DIN11864 JN-FL 23 2002 Welded Hose Nipple For Water
The primary component of a rubber joint is the rubber itself. Various types of rubber compounds may be used, such as EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer), neoprene, natural rubber, or other synthetic rubber materials. The rubber provides flexibility, resilience, and the ability to absorb movement and vibrations. The bellows or flexing element is the accordion-like structure that allows the rubber joint to flex and absorb movements in multiple directions. Flanges and end connections that facilitate the attachment of the joint to other components in the piping system. Flanges are commonly made of metal and are either bonded or bolted to the rubber joint.
The primary function of a rubber joint is to absorb movements and vibrations in a system. The flexible bellows or accordion-like structure of the rubber joint allows it to expand, contract, and bend in multiple directions, accommodating axial, lateral, and angular movements.
When pipes or components in a system undergo thermal expansion or contraction, the rubber joint's axial flexibility allows it to elongate or compress accordingly, preventing undue stress on the connected components. Rubber joints can also accommodate lateral movements, angular movements, thermal expansion and contraction.
Working principle

The working principle of rubber joints involves their flexibility and ability to absorb movements in multiple directions. This makes them essential components in piping systems and other applications where dynamic forces, thermal changes, and vibrations are present. Properly functioning rubber joints contribute to the overall integrity and longevity of the connected system.
Stainless Steel Hose Adapter Specification Chart

| Material | SS304, SS316L | |
| Diameter | 1 "to 24" | |
| Length | 95mm to 265mm | |
| Standard | DIN, ISO, ASTM | |
| Max pressure | up to 10 bar | |
| Standard | 3A/SMS/DIN/ISO2037/ISO1127/AS1528/BS/BPE/IDF | |
| Working temperatur | -15℃ to +160℃ | |
| End connections | Flanged, Threaded | |
| Gasket or seals | Viton, PTFEE | |
Features

● Flexible movements and vibrations
● Vibration isolation: Rubber joints help reduce the transmission of vibrations to connected components.
● Noise reduction because of the isolated vibrations
● Misalignment compensation
● Thermal expansion and contraction
● Corrosion protection
● Cost effective solution
● Protection of the eqipment
Application

Rubber joints find their application where movement, vibration, and flexibility are critical considerations. Some common applications of rubber joints include are Heating and cooling devices, Materials handling technologies, Water pipes, Desalination plants, Compressors, Blowers and fans, Cement industry, Chemical industry, Glass industy, Wood-processing industry, Pulp and paper industry, Railed vehicles, Refineries, Shipbuilding, Steel mills, Sugar industry.
Feature and Specification

Stainless Steel Hose Adapter Specification Chart

| Material | SS304, SS316L | |
| Diameter | 1 "to 24" | |
| Length | 95mm to 265mm | |
| Standard | DIN, ISO, ASTM | |
| Max pressure | up to 10 bar | |
| Standard | 3A/SMS/DIN/ISO2037/ISO1127/AS1528/BS/BPE/IDF | |
| Working temperatur | -15℃ to +160℃ | |
| End connections | Flanged, Threaded | |
| Gasket or seals | Viton, PTFEE | |
Features

● Flexible movements and vibrations
● Vibration isolation: Rubber joints help reduce the transmission of vibrations to connected components.
● Noise reduction because of the isolated vibrations
● Misalignment compensation
● Thermal expansion and contraction
● Corrosion protection
● Cost effective solution
● Protection of the eqipment
304 Stainless Steel Sanitary DIN11864 JN-FL 23 2002 Welded Hose Nipple For Water
The primary component of a rubber joint is the rubber itself. Various types of rubber compounds may be used, such as EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer), neoprene, natural rubber, or other synthetic rubber materials. The rubber provides flexibility, resilience, and the ability to absorb movement and vibrations. The bellows or flexing element is the accordion-like structure that allows the rubber joint to flex and absorb movements in multiple directions. Flanges and end connections that facilitate the attachment of the joint to other components in the piping system. Flanges are commonly made of metal and are either bonded or bolted to the rubber joint.
The primary function of a rubber joint is to absorb movements and vibrations in a system. The flexible bellows or accordion-like structure of the rubber joint allows it to expand, contract, and bend in multiple directions, accommodating axial, lateral, and angular movements.
When pipes or components in a system undergo thermal expansion or contraction, the rubber joint's axial flexibility allows it to elongate or compress accordingly, preventing undue stress on the connected components. Rubber joints can also accommodate lateral movements, angular movements, thermal expansion and contraction.
Working principle

The working principle of rubber joints involves their flexibility and ability to absorb movements in multiple directions. This makes them essential components in piping systems and other applications where dynamic forces, thermal changes, and vibrations are present. Properly functioning rubber joints contribute to the overall integrity and longevity of the connected system.
Stainless Steel Hose Adapter Specification Chart

| Material | SS304, SS316L | |
| Diameter | 1 "to 24" | |
| Length | 95mm to 265mm | |
| Standard | DIN, ISO, ASTM | |
| Max pressure | up to 10 bar | |
| Standard | 3A/SMS/DIN/ISO2037/ISO1127/AS1528/BS/BPE/IDF | |
| Working temperatur | -15℃ to +160℃ | |
| End connections | Flanged, Threaded | |
| Gasket or seals | Viton, PTFEE | |
Features

● Flexible movements and vibrations
● Vibration isolation: Rubber joints help reduce the transmission of vibrations to connected components.
● Noise reduction because of the isolated vibrations
● Misalignment compensation
● Thermal expansion and contraction
● Corrosion protection
● Cost effective solution
● Protection of the eqipment
Application

Rubber joints find their application where movement, vibration, and flexibility are critical considerations. Some common applications of rubber joints include are Heating and cooling devices, Materials handling technologies, Water pipes, Desalination plants, Compressors, Blowers and fans, Cement industry, Chemical industry, Glass industy, Wood-processing industry, Pulp and paper industry, Railed vehicles, Refineries, Shipbuilding, Steel mills, Sugar industry.

Feature and Specification


Stainless Steel Hose Adapter Specification Chart

| Material | SS304, SS316L | |
| Diameter | 1 "to 24" | |
| Length | 95mm to 265mm | |
| Standard | DIN, ISO, ASTM | |
| Max pressure | up to 10 bar | |
| Standard | 3A/SMS/DIN/ISO2037/ISO1127/AS1528/BS/BPE/IDF | |
| Working temperatur | -15℃ to +160℃ | |
| End connections | Flanged, Threaded | |
| Gasket or seals | Viton, PTFEE | |
Features

● Flexible movements and vibrations
● Vibration isolation: Rubber joints help reduce the transmission of vibrations to connected components.
● Noise reduction because of the isolated vibrations
● Misalignment compensation
● Thermal expansion and contraction
● Corrosion protection
● Cost effective solution
● Protection of the eqipment